Table of Contents
ToggleTable of Contents
- Introduction
- What Does “Ranking a Website” Mean?
- The Three Main Steps of Search Engines
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Ranking
- Crawling
- Key Factors That Decide Website Rankings
- Relevance of Content
- Backlinks and Authority
- User Experience (UX)
- Page Speed and Mobile Friendliness
- Search Intent
- Freshness of Content
- Relevance of Content
- Real-Life Examples of Website Ranking
- Why Different Searches Show Different Results
- FAQs on How Search Engines Rank Websites
- Final Thoughts
Introduction
Have you ever typed something into Google and wondered, “How did Google decide which website to show first?” That’s exactly what website ranking is all about. Search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo don’t just throw random pages at you. They carefully analyze billions of web pages and pick the ones they believe will help you most. The process is complex, but in this article, we’ll break it down into simple words so anyone can understand it.
What Does “Ranking a Website” Mean?
When we say a website is “ranked,” we’re talking about its position on the search engine results page (SERP).
For example:
- If your website appears #1 when someone searches “best coffee shop in New York,” it means Google finds your site the most useful for that query.
- If your site is on page 10 of Google, most people will never see it.
So, the higher you rank, the more people find your website.
The Three Main Steps of Search Engines
When we say a website is “ranked,” we’re talking about its position on the search engine results page (SERP).
For example:
- If your website appears #1 when someone searches “best coffee shop in New York,” it means Google finds your site the most useful for that query.
- If your site is on page 10 of Google, most people will never see it.
So, the higher you rank, the more people find your website.
The Three Main Steps of Search Engines
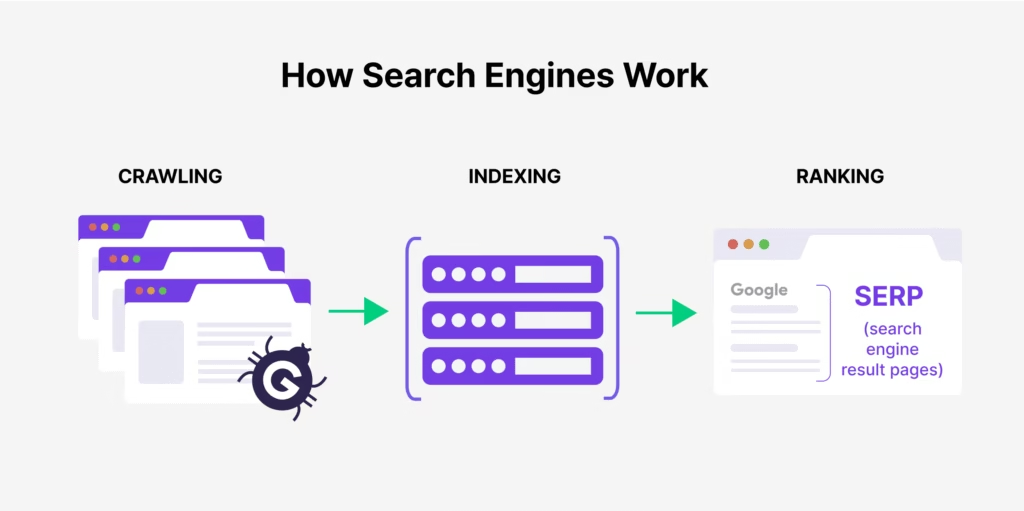
Before ranking your site, search engines go through three important steps:
1. Crawling
Think of crawling like a search engine’s “discovery tour.” Google uses programs called crawlers or bots that travel across the internet, visiting websites and reading their pages.
- If your site is new and not linked anywhere, it may not get crawled quickly.
- That’s why submitting a sitemap to Google Search Console helps.
2. Indexing
After crawling, Google stores information about your website in its giant library, called the index.
- If your site is in the index, it means Google remembers it.
- If not, it won’t show up in search results.
For example, if you write a blog about “healthy breakfast ideas,” Google will index your content under topics like food, health, and recipes.
3. Ranking
This is the final step where Google decides which indexed page should appear first. Out of thousands of possible results, Google uses its algorithm (a set of rules and formulas) to rank pages.
Key Factors That Decide Website Rankings
Search engines look at hundreds of ranking factors, but let’s focus on the most important ones.
Relevance of Content
Google checks if your page actually answers the user’s question.
- Example: If someone searches “how to bake a chocolate cake” and your blog is about pasta, it won’t rank.
- Using the right keywords naturally in your text helps search engines understand your topic.
Backlinks and Authority
A backlink is when another website links to yours. Search engines see backlinks as votes of confidence.
- If many trusted sites link to you, Google believes your content is valuable.
- Example: A health article cited by Mayo Clinic or WebMD will likely rank higher than one with no references.
User Experience (UX)
If visitors land on your page but leave within seconds, Google thinks your site wasn’t helpful.
Good UX includes:
- Easy navigation
- Clear design
- No annoying pop-ups
Page Speed and Mobile Friendliness
Most people now use mobile phones to search. If your site loads slowly or doesn’t fit on a mobile screen, your ranking drops.
Google even provides tools like PageSpeed Insights to check this.
Search Intent
This is one of the most important factors. Search engines try to understand why someone is searching.
For example:
- “Best laptop 2025” → The intent is to compare and maybe buy.
- “History of the Internet” → The intent is to learn, not to buy.
If your content matches the intent, you’ll rank higher.
Freshness of Content
Google prefers up-to-date information for time-sensitive topics.
- Example: An article on “Best SEO Tools 2025” will outrank “Best SEO Tools 2018.”
Real-Life Examples of Website Ranking
Imagine two websites about Italian restaurants in Chicago.
- Website A has:
- Detailed menu
- Customer reviews
- Mobile-friendly design
- Local backlinks from Chicago food blogs
- Detailed menu
- Website B has:
- Outdated menu
- No reviews
- Slow loading speed
- Outdated menu
Guess which one ranks higher? → Website A.
Google sees it as more relevant, authoritative, and user-friendly.
Why Different Searches Show Different Results
Not everyone sees the same results because Google personalizes rankings based on:
- Your location (searching “pizza near me” in New York vs. Los Angeles gives different results).
- Your search history.
- The device you use (mobile vs. desktop).
That’s why SEO experts say, “There’s no one-size-fits-all ranking.”
FAQs on How Search Engines Rank Websites
1. How long does it take to rank a website?
It depends. Some sites rank in a few weeks, while competitive niches may take months.
2. Do keywords still matter in 2025?
Yes, but not like before. Google looks at the overall meaning (semantic search) rather than just exact keywords.
3. Can I rank without backlinks?
Yes, but backlinks make it much easier. High-quality content can sometimes rank on its own for low-competition searches.
4. Why does my website rank on page 2, not page 1?
It could be due to stronger competitors, a lack of backlinks, or a poor user experience.
5. What is the #1 ranking factor?
There’s no single factor. Google uses a mix of content quality, authority, and user signals.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how search engines rank websites isn’t just for SEO professionals—it’s for anyone who wants their content to be discovered online.
The process starts with crawling and indexing, but the real competition happens in ranking. Your website’s position depends on how well your content matches the user’s intent, how much authority your site has, and how good the overall user experience is.
If you want to improve your site’s ranking, focus on:
- Creating helpful, original content
- Building trustworthy backlinks
- Making your site fast and mobile-friendly
- Updating content to stay fresh and relevant
At the end of the day, Google’s mission is simple: to give people the best possible answers. If your website helps people, rankings will follow.
✅ Suggested Tags: SEO, Website Ranking, Google Ranking, Search Engine Optimization, SEO Basics, Digital Marketing
✅ External References: